Architecture
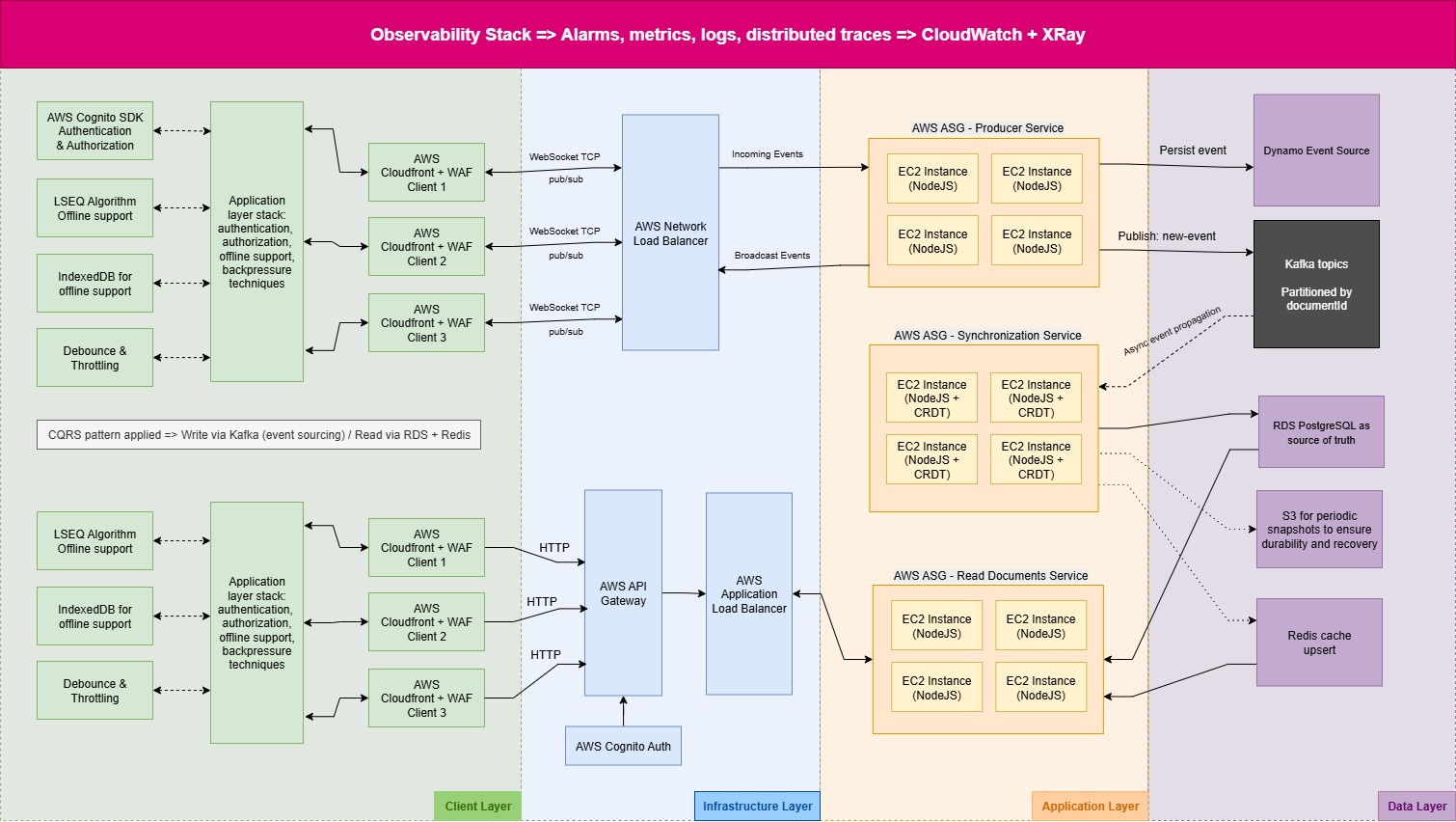
General diagram
Real-time LSEQ Operation Flow with WebSocket, Kafka, and CRDT Sync
1. Client Operation Submission:
When a client generates a new LSEQ operation, it is sent via WebSocket.
2. Load Balancing & Scaling:
The operation passes through the AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB) and reaches an Auto Scaling Group (ASG) of EC2 instances that are subscribed to the WebSocket channel.
3. Broadcast to Other Clients:
The WebSocket channel propagates the operation to all other connected clients in real-time, ensuring immediate local updates.
4. Asynchronous Sync & Merge:
The operation is also published to a Kafka topic for downstream services responsible for CRDT-based conflict resolution and state merging.
5. Persistent Storage:
After merging, the final state is persisted in PostgreSQL, ensuring durable storage and eventual consistency across clients.
6. Key Benefits:
- Real-time collaboration with low latency.
- Offline operations can be queued locally and synchronized later.
- CRDT ensures conflict-free merging of concurrent edits.
Kafka decouples the real-time channel from persistence and background processing.
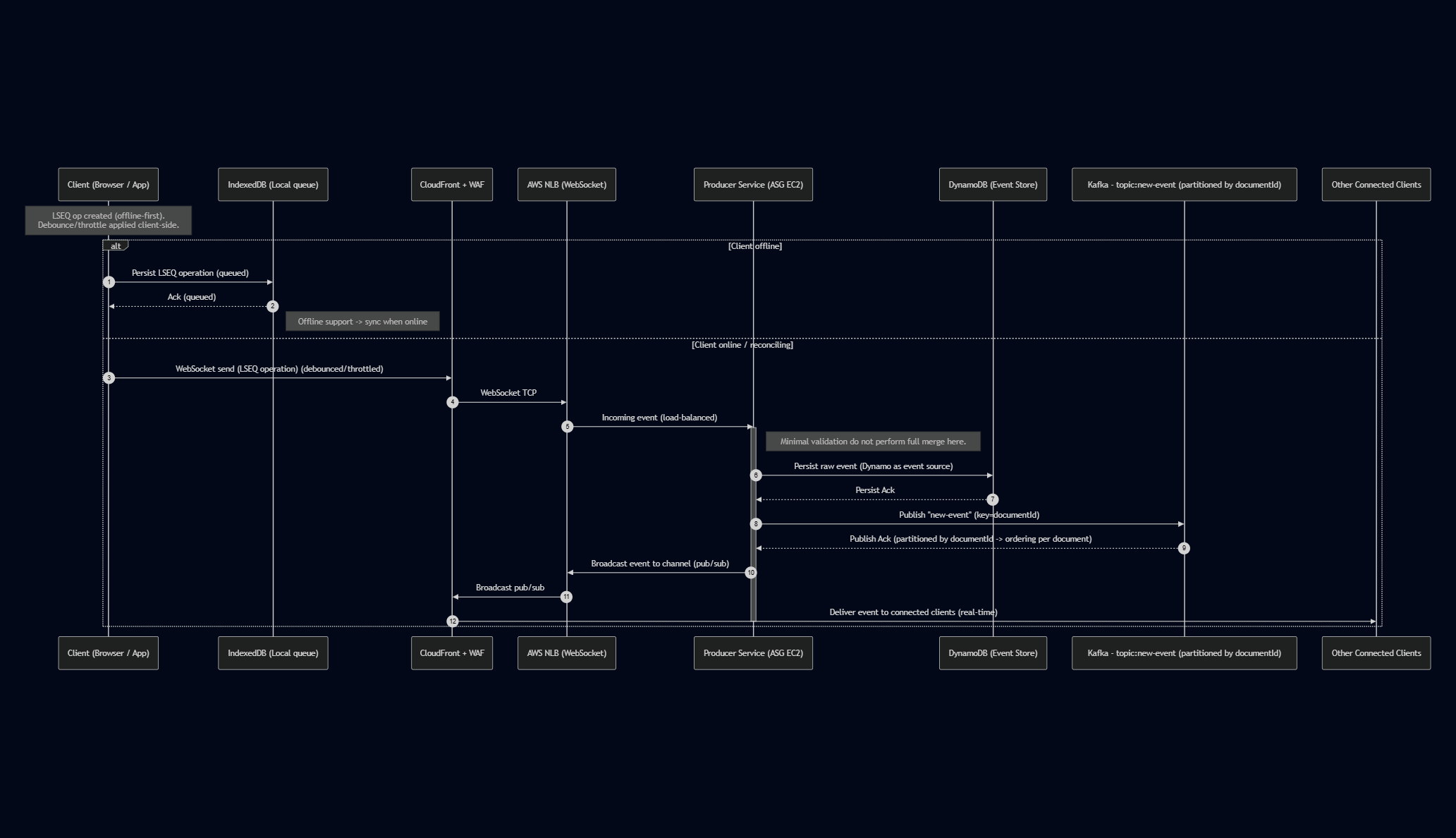
Sequence diagram - Publishing new event on WebSocket
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant Client as Client (Browser / App)
participant IndexedDB as IndexedDB (Local queue)
participant CF as CloudFront + WAF
participant NLB as AWS NLB (WebSocket)
participant Producer as Producer Service (ASG EC2)
participant Dynamo as DynamoDB (Event Store)
participant Kafka as Kafka - topic:new-event (partitioned by documentId)
participant OtherClients as Other Connected Clients
Note over Client: LSEQ op created (offline-first).<br> Debounce/throttle applied client-side.
alt Client offline
Client->>IndexedDB: Persist LSEQ operation (queued)
IndexedDB-->>Client: Ack (queued)
Note right of IndexedDB: Offline support -> sync when online
else Client online / reconciling
Client->>CF: WebSocket send (LSEQ operation) (debounced/throttled)
CF->>NLB: WebSocket TCP
NLB->>Producer: Incoming event (load-balanced)
activate Producer
Note right of Producer: Minimal validation do not perform full merge here.
Producer->>Dynamo: Persist raw event (Dynamo as event source)
Dynamo-->>Producer: Persist Ack
Producer->>Kafka: Publish "new-event" (key=documentId)
Kafka-->>Producer: Publish Ack (partitioned by documentId -> ordering per document)
Producer->>NLB: Broadcast event to channel (pub/sub)
NLB->>CF: Broadcast pub/sub
CF->>OtherClients: Deliver event to connected clients (real-time)
deactivate Producer
end
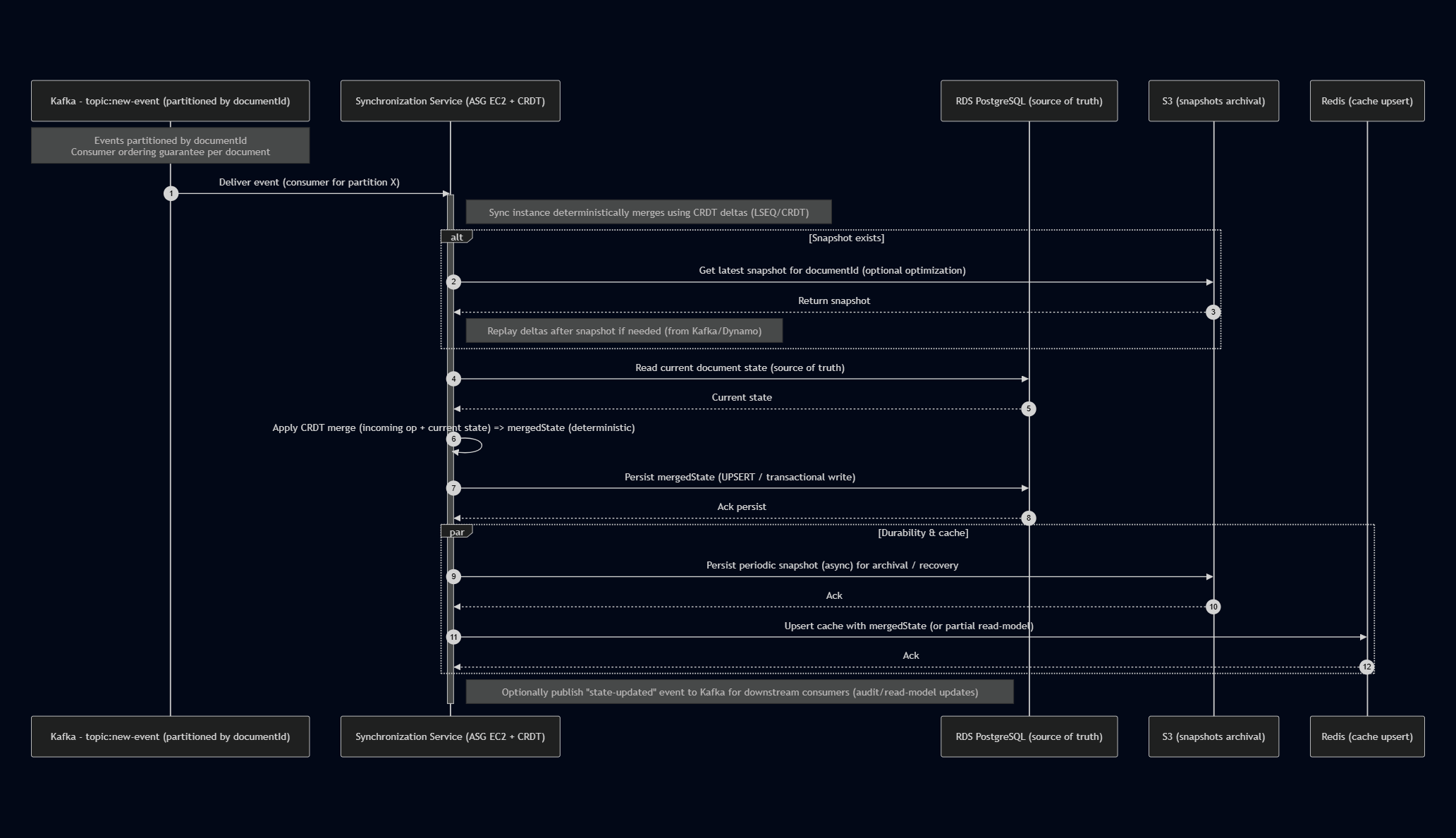
Sequence diagram - Synchronization service
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant Kafka as Kafka - topic:new-event (partitioned by documentId)
participant Sync as Synchronization Service (ASG EC2 + CRDT)
participant RDS as RDS PostgreSQL (source of truth)
participant S3 as S3 (snapshots archival)
participant Redis as Redis (cache upsert)
Note over Kafka: Events partitioned by documentId<br>Consumer ordering guarantee per document
Kafka->>Sync: Deliver event (consumer for partition X)
activate Sync
Note right of Sync: Sync instance deterministically merges using CRDT deltas (LSEQ/CRDT)
alt Snapshot exists
Sync->>S3: Get latest snapshot for documentId (optional optimization)
S3-->>Sync: Return snapshot
Note right of Sync: Replay deltas after snapshot if needed (from Kafka/Dynamo)
end
Sync->>RDS: Read current document state (source of truth)
RDS-->>Sync: Current state
Sync->>Sync: Apply CRDT merge (incoming op + current state) => mergedState (deterministic)
Sync->>RDS: Persist mergedState (UPSERT / transactional write)
RDS-->>Sync: Ack persist
par Durability & cache
Sync->>S3: Persist periodic snapshot (async) for archival / recovery
S3-->>Sync: Ack
Sync->>Redis: Upsert cache with mergedState (or partial read-model)
Redis-->>Sync: Ack
end
Note right of Sync: Optionally publish "state-updated" event to Kafka for downstream consumers (audit/read-model updates)
deactivate Sync
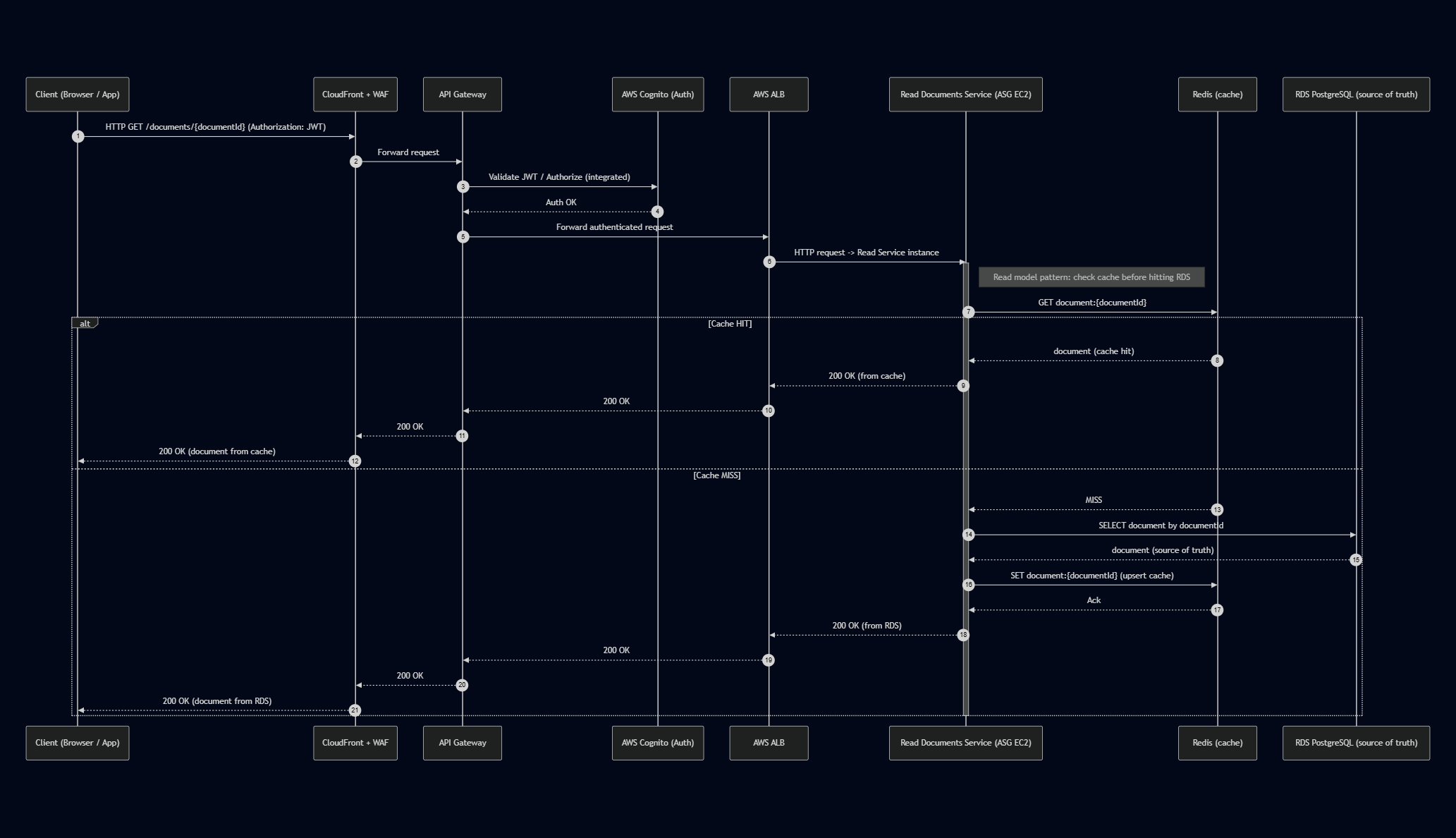
Sequence diagram - Read documents service
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
participant Client as Client (Browser / App)
participant CF as CloudFront + WAF
participant APIGW as API Gateway
participant Cognito as AWS Cognito (Auth)
participant ALB as AWS ALB
participant ReadSvc as Read Documents Service (ASG EC2)
participant Redis as Redis (cache)
participant RDS as RDS PostgreSQL (source of truth)
Client->>CF: HTTP GET /documents/{documentId} (Authorization: JWT)
CF->>APIGW: Forward request
APIGW->>Cognito: Validate JWT / Authorize (integrated)
Cognito-->>APIGW: Auth OK
APIGW->>ALB: Forward authenticated request
ALB->>ReadSvc: HTTP request -> Read Service instance
activate ReadSvc
Note right of ReadSvc: Read model pattern: check cache before hitting RDS
ReadSvc->>Redis: GET document:{documentId}
alt Cache HIT
Redis-->>ReadSvc: document (cache hit)
ReadSvc-->>ALB: 200 OK (from cache)
ALB-->>APIGW: 200 OK
APIGW-->>CF: 200 OK
CF-->>Client: 200 OK (document from cache)
else Cache MISS
Redis-->>ReadSvc: MISS
ReadSvc->>RDS: SELECT document by documentId
RDS-->>ReadSvc: document (source of truth)
ReadSvc->>Redis: SET document:{documentId} (upsert cache)
Redis-->>ReadSvc: Ack
ReadSvc-->>ALB: 200 OK (from RDS)
ALB-->>APIGW: 200 OK
APIGW-->>CF: 200 OK
CF-->>Client: 200 OK (document from RDS)
end
deactivate ReadSvc